2023
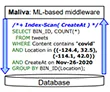
We consider data-visualization systems where a middleware layer translates a frontend request to a SQL query to a backend database to compute visual results. We study the problem of answering a visualization request within a limited time due to the responsiveness requirement. We explore optimization options of rewriting an original query by adding hints and/or doing approximations so that the total time is within the time constraint. We develop a novel middleware solution called Maliva based on machine learning (ML) techniques. It applies the Markov Decision Process (MDP) model to decide how to rewrite queries and uses instances to train an agent to make a sequence of decisions judiciously for an online request. We give a full specification of the technique, including how to construct an MDP model, how to train an agent, and how to use approximation rewriting options. Our experiments on both real and synthetic datasets show that Maliva performs significantly better than a baseline solution that does not do any rewriting, in terms of both the probability of serving requests interactively and query execution time.
2022
Pixel reconstruction filters play an important role in physics-based rendering and have been thoroughly studied. In physics-based differentiable rendering, however, the proper treatment of pixel filters remains largely under-explored. We present a new technique to efficiently differentiate pixel reconstruction filters based on the path-space formulation. Specifically, we formulate the pixel boundary integral that models discontinuities in pixel filters and introduce new antithetic sampling methods that support differentiable path sampling methods, such as adjoint particle tracing and bidirectional path tracing. We demonstrate both the need and efficacy of antithetic sampling when estimating this integral, and we evaluate its effectiveness across several differentiable- and inverse-rendering settings.
We study the problem of computing a spatial scatterplot on a large dataset for arbitrary zooming/panning queries. We introduce a general framework called “Rainbow” that generates a high-quality scatterplot for a given result-size budget. Rainbow augments a spatial index with judiciously selected representative points offline. To answer a query, Rainbow traverses the index top-down and selects representative points with a good quality until the result-size budget is reached. We experimentally demonstrate the effectiveness of Rainbow.