2025
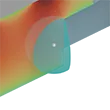
Monte Carlo methods based on the walk on spheres (WoS) algorithm offer a parallel, progressive, and output-sensitive approach for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) in complex geometric domains. Building on this foundation, the walk on stars (WoSt) method generalizes WoS to support mixed Dirichlet, Neumann, and Robin boundary conditions. However, accurately computing spatial derivatives of PDE solutions remains a major challenge: existing methods exhibit high variance and bias near the domain boundary, especially in Neumann-dominated problems. We address this limitation with a new extension of WoSt specifically designed for derivative estimation. Our method reformulates the boundary integral equation (BIE) for Poisson PDEs by directly leveraging the harmonicity of spatial derivatives. Combined with a tailored random-walk sampling scheme and an unbiased early termination strategy, we achieve significantly improved accuracy in derivative estimates near the Neumann boundary. We further demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach across various tasks, including recovering the non-unique solution to a pure Neumann problem with reduced bias and variance, constructing divergence-free vector fields, and optimizing parametrically defined boundaries under PDE constraints.
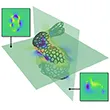
Walk on stars (WoSt) has shown its power in being applied to Monte Carlo methods for solving partial differential equations, but the sampling techniques in WoSt are not satisfactory, leading to high variance. We propose a guiding-based importance sampling method to reduce the variance of WoSt. Drawing inspiration from path guiding in rendering, we approximate the directional distribution of the recursive term of WoSt using online-learned parametric mixture distributions, decoded by a lightweight neural field. This adaptive approach enables importance sampling the recursive term, which lacks shape information before computation. We introduce a reflection technique to represent guiding distributions at Neumann boundaries and incorporate multiple importance sampling with learnable selection probabilities to further reduce variance. We also present a practical GPU implementation of our method. Experiments show that our method effectively reduces variance compared to the original WoSt, given the same time or the same sample budget.
2024
The Poisson equation is an important partial differential equation (PDE) with numerous applications in physics, engineering, and computer graphics. Conventional solutions to the Poisson equation require discretizing the domain or its boundary, which can be very expensive for domains with detailed geometries. To overcome this challenge, a family of grid-free Monte Carlo solutions has recently been developed. By utilizing walk-on-sphere (WoS) processes, these techniques are capable of efficiently solving the Poisson equation over complex domains.
In this paper, we introduce a general technique that differentiates solutions to the Poisson equation with Dirichlet boundary conditions. Specifically, we devise a new boundary-integral formulation for the derivatives with respect to arbitrary parameters including shapes of the domain. Further, we develop an efficient walk-on-spheres technique based on our new formulation — including a new approach to estimate normal derivatives of the solution field. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our technique over baseline methods using several synthetic examples.
2021
This paper introduces a new family of hybrid estimators aimed at controlling the efficiency of Monte Carlo computations in particle transport problems. In this context, efficiency is usually measured by the figure of merit (FOM) given by the inverse product of the estimator variance Var[ξ] and the run time T: FOM := (Var[ξ], T)-1. Previously, we developed a new family of transport-constrained unbiased radiance estimators (T-CURE) that generalize the conventional collision and track length estimators and provide 1--2 orders of magnitude additional variance reduction. However, these gains in variance reduction are partly offset by increases in overhead time, lowering their computational efficiency. Here we show that combining T-CURE estimation with conventional terminal estimation within each individual biography can moderate the efficiency of the resulting "hybrid" estimator without introducing bias in the computation. This is achieved by treating only the refractive interface crossings with the extended next event estimator, and all others by standard terminal estimators. This is because when there are index-mismatched interfaces between the collision location and the detector, the T-CURE computation rapidly becomes intractable due to the large number of refractions and reflections that can arise. We illustrate the gains in efficiency by comparing our hybrid strategy with more conventional estimation methods in a series of multi-layer numerical examples.
2016
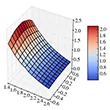
Monte Carlo methods provide the "gold standard" computational technique for solving biomedical problems but their use is hindered by the slow convergence of the sample means. An exponential increase in the convergence rate can be obtained by adaptively modifying the sampling and weighting strategy employed. However, if the radiance is represented globally by a truncated expansion of basis functions, or locally by a region-wise constant or low degree polynomial, a bias is introduced by the truncation and/or the number of subregions. The sheer number of expansion coefficients or geometric subdivisions created by the biased representation then partly or entirely offsets the geometric acceleration of the convergence rate. As well, the (unknown amount of) bias is unacceptable for a gold standard numerical method. We introduce a new unbiased estimator of the solution of radiative transfer equation (RTE) that constrains the radiance to obey the transport equation. We provide numerical evidence of the superiority of this Transport-Constrained Unbiased Radiance Estimator (T-CURE) in various transport problems and indicate its promise for general heterogeneous problems.